The Complete Guide to Social-Emotional Learning
Creating safe learning environments requires an emphasis on social and emotional safety as well as physical safety. A critical component is a solid, evidence-based social-emotional learning (SEL) curriculum that helps students succeed academically, socially and emotionally. Aligned with the core competencies set by CASEL, one of the pioneers of social-emotional learning, Navigate360 SEL provides crucial character development and restorative curriculum to students of all ages, genders and cultures.
This guide will:

Discover how SEL can help your students succeed academically, socially and emotionally with our Complete Guide to Social-Emotional Learning.
1. The Foundations of Social-Emotional Learning (SEL)
a. What Is Social Emotional Learning?
Social-emotional learning (SEL) is a framework that encourages students to develop positive self-identities, manage complex emotions, navigate a variety of social situations, build strong relationships with others, and develop empathetic worldviews. It fosters a healthy and trusting learning environment that can improve student behavior, address inequities in the classroom, and set students up for success both academically and personally. In short, SEL is a crucial aspect of childhood development that should be a part of every district and school curriculum.
The truth is that nobody is born understanding how to perfectly manage their emotions and handle complex challenges. Instead, those skills must be taught and taught from a place of openness and positivity. Students must feel free to express themselves, make mistakes, and ask questions in order to develop their social-emotional skills. In turn, they will be able to better handle challenges as they arise, understand and empathize with those who are different from them, and achieve the goals they set. This allows them to succeed in school and then later in college, their careers, and their lives as a whole.
b. What Are the Benefits of SEL Curricula?
Students are dealing with a lot these days. From living through a global pandemic that threw their lives into upheaval to grappling with cyberbullying and all its iterations, kids without the social and emotional skills to handle these stressors can fall behind in school, exhibit challenging behaviors, and withdraw from relationships. But in classrooms where social-emotional learning is a priority, students learn crucial skills to thrive in school and in life. According to more than two decades of research, SEL can:
- Improve academic performance and classroom behavior
- Help students better manage anxiety, depression, and stress levels
- Encourage students to have positive attitudes about themselves and the people around them
- Impact students over the long term, helping them in college and beyond
A high-quality SEL curriculum creates an avenue for students to explore their emotions and deepen their understanding of others. While it can be easy to push SEL aside for core academic requirements, the benefits are clear. Developing a child’s inner sense of self and encouraging positive social-emotional learning only serve to improve academics in the long run. And there’s an economic benefit, too. According to the Journal of Cost-Benefit Analysis, for every $1 invested in SEL programs, there is a return of $11.
c. Why SEL Is Important for Students Now
Students today have more external pressures than ever before. In 2020 alone, they dealt with the COVID-19 pandemic that dramatically shifted learning, bringing it out of the classroom and into the home with online schooling. Not to mention, an economic crisis forced many parents out of work while a racial justice movement caused societal reckoning. These unique challenges can be difficult to navigate without strong social-emotional skills. Consider some of the many stressors they are dealing with:
- Cyberbullying
- Peer pressure and social stress
- Body image issues
- Academic performance
- Catching up academically
- Adjusting to life during and after COVID-19
- Anxiety and depression
A recent poll conducted by Navigate360 and John Zogby Strategies uncovered startling statistics about how teenagers are feeling these days about their physical, social, and emotional needs. For example, 61% of teens said they feel more concerned about their physical and emotional safety than they did six months prior, and 54% believe that getting COVID-19 or experiencing a violent incident could prevent them from achieving their goals.
“Maslow before Bloom” has become a popular phrase in academic circles. It’s the idea that educators must meet the basic needs of students in order to develop an effective educational learning environment. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs is a five-tier model of the basic needs of humans—once each basic need is met, individuals can move on to higher-level thinking and meeting more advanced needs. Bloom’s taxonomy focuses primarily on learning. The “Maslow before Bloom” concept describes how students must have their basic health and safety needs met in order to learn effectively. If a student is hungry, worried about bullying in the classroom, or dealing with trauma, then their mind is not biologically ready to handle advanced, higher-order learning.
That’s why students need SEL now more than ever. It gives them tools to better understand themselves and how they respond to stressful situations, and helps them develop strategies to handle external and internal challenges. In turn, they will be able to focus on academics as their social/emotional needs are met.

Quantify SEL’s Positive Outcomes for Students & Schools
Research consistently shows that social-emotional learning programs have positive effects that result in improved safety and security for schools. According to the Journal of Cost-Benefit Analysis, for every $1 invested in SEL programs, there is a return of $11. (Belfield et al, 2015).
d. Why SEL Is Important for Students’ Futures
Emotional intelligence, interpersonal skills, stress tolerance and resilience are some of the leading job skills that employers will be looking for in the future. What’s more, the job market is changing so rapidly that, according to a report by Dell Technologies, 85% of the jobs that will exist in 2030 haven’t been invented yet. With this in mind, it’s easy to see why SEL is crucial for students’ futures. What awaits them in the future is uncertain, but it’s clear that having strong social and emotional skills will be necessary. Being able to work well with others, see opposing viewpoints, think critically, problem-solve effectively, and achieve goals are all skills that students learn from SEL, which will equip them well for the future.
e. Expected Outcomes of Well-Executed SEL Programs
While helping kids become well-rounded individuals who understand their social and emotional needs is a worthwhile goal, so is teaching traditional academic curriculum to impart essential knowledge to ensure students become productive members of society. It’s natural for educators to be concerned that implementing a social-emotional curriculum will be just one more thing on their already overcrowded plate. The good news is that high-quality SEL instruction can be integrated into existing programs and that SEL actually helps students become more engaged and excited about learning. Take a look at some of the ways well-executed SEL programs have a positive academic impact:
- Improved student engagement
- Better content absorption
- Increased knowledge retention on a long-term basis
- Improved social behavior and fewer conduct problems
- Enhanced academic performance
In turn, these positive outcomes in the classroom allow students to thrive and cultivate a curious growth mindset that serves them well in the future. A social-emotional foundation can influence students’ college and career readiness, ensuring they develop the self-management skills, social skills, and self-confidence that are required in post-secondary life. These students also go on to become more engaged citizens who have better mental health, more positive relationships, and career success.
f. Learn More About SEL
SEL is a broad subject with a tremendous amount of positive implications for students and educators. If you’d like to learn more about this topic, Navigate360 offers a free on-demand webinar called “Supporting the Health & Wellbeing of Students Through Social-Emotional Learning” that features well-versed subject-matter experts. This webinar includes:
- An introduction to the topic of SEL
- A discussion about the current landscape of student health and wellbeing
- Recent sentiments about how students are feeling about their physical and emotional safety
- How an effective SEL program can better support students and educators during difficult times
In addition to the valuable information found in this webinar, our  is available as well.
is available as well. 
.
Get expert insights on what schools are looking for in SEL and how to implement a program that stands the test of time.
2. Introducing: CASEL
a. Who Is CASEL?
The Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning (CASEL) provides trusted, evidence-based resources for K-12 educators and policy leaders. Over two decades ago, CASEL developed its SEL framework and has been dedicated to implementing SEL in schools and districts nationwide ever since. Recently, in the fall of 2020, CASEL updated its framework and SEL definition to better affirm the experiences and identities of all children—notably, those who have traditionally been marginalized in academic spaces. These updates come after decades of research and changes to SEL practices and aim to create more caring and just schools for all students. Providing equitable learning environments that allow all students to thrive is the ultimate goal of CASEL’s SEL framework.
b. Why Is it Important for an SEL Curriculum to Align With the 5 CASEL Core Competencies?
The five CASEL competencies are at the core of the SEL framework and provide the foundation for high-quality SEL curricula. They are based on an immense amount of research from the pioneers of SEL education. These competencies pinpoint five interrelated areas that advance a student’s learning and development and can be applied from preschool to high school and beyond. They help educators understand what is needed from their students to encourage academic success, civic engagement, health and wellness, and more.
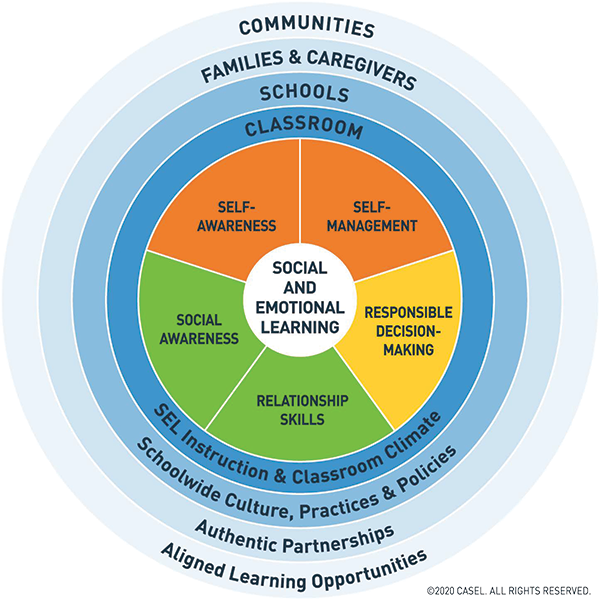
The five CASEL core competencies are:
- Self-awareness – Students understand their own culture, language, beliefs and values. They recognize their emotions, understand their needs and are aware of their strengths and limitations.
- Self-management – Students know how their thoughts, feelings and actions are influenced by their beliefs and value systems. They can monitor their behavior and understand how to effectively respond in different situations.
- Social awareness – Students have empathy for others. They understand that everyone has a different worldview and they can appreciate the perspectives of others.
- Relationship skills – Students form positive, healthy relationships with others, including those who may look, act or behave differently than they do. They can effectively deal with conflict and work with others toward a common goal.
- Responsible decision making –Students recognize they have an impact on the people around them and act accordingly. They also understand the differences between good and bad decisions.
c. What Other Factors Are Important in an SEL Curriculum? Why?
S.A.F.E. Classroom Environments
The acronym S.A.F.E. is the cornerstone of a well-executed SEL program. It stands for:
- Sequenced – Activities should be coordinated and connected and build upon one another to develop the social-emotional skills students need.
- Active – Educators should develop active forms of learning, such as roleplaying, to help students master new skills.
- Focused – There should be time set aside to develop the personal and social skills of students.
- Explicit – The program should clearly state which social-emotional skills are being learned.
Neuroscience Research
Recent neuroscience research has delivered startling results about the ways SEL impacts cognitive learning. Johns Hopkins University, a leader in neuroeducation, is the birthplace of Dr. Mariale Hardiman’s Brain-Targeted Teaching® (BTT) model that has uncovered the links between cognitive processes and SEL. BTT is an instructional framework that consists of six stages crucial to the learning process. And the very first stage? Setting up a positive emotional climate.
At the base of the brain, just above the brainstem, is the limbic system, which is responsible for emotional responses. All information a student receives is first processed through the limbic system before moving on to the frontal lobe, or the cognitive area of the brain. This means that a student who is stressed, depressed, anxious or otherwise emotionally distressed cannot process information appropriately, which impacts their learning. Developing educational environments that emphasize positive emotions, provide a space of belonging and community, and allow students to connect emotionally with their studies are crucial to optimal academic performance.
d. Learn More About CASEL
To learn more about CASEL, its mission and how it has developed SEL competencies to help children grow into well-rounded adults, feel free to check out this helpful brochure.

Discover SEL that Meets K-12’s Highest, Most Accepted Standards
3. FAQs: Important Factors When Launching a Successful SEL Curriculum
a. Are There Standards/Guidelines at the State Level for SEL programs?
Currently, 29 states have established specific SEL standards or requirements. These standards allow educators to understand exactly what students should be learning from an SEL curriculum and how to apply it in the classroom. However, it should be noted that just because a state doesn’t have specific SEL guidelines, that doesn’t mean they don’t promote SEL. It simply means they haven’t codified definitive standards for students. You can find a list of the standards by state here.
Additionally, a handful of states have enacted SEL legislation to establish advisory boards, commissions, committees, and task forces to promote, expand, and set up SEL programs in K-12 schools. For a list of the specific state legislation that has been enacted, click here.
b. How Is SEL Being Evaluated at a District Level?
Currently, there is no gold-standard measuring tool for evaluating SEL at the school district level. District leaders can create their own SEL evaluation programs that use the CASEL core competency framework as a guide. School districts can also work with SEL researchers to evaluate their programs. For example, Navigate360 regularly partners with school districts to engage in SEL research. What’s more, in SEL for Students, there is a CASEL-developed, pre– and post-measurement tool that was established in association with the University of Illinois and the Washoe County School District, a helpful addition for evaluating the effectiveness of an SEL program in a school.
c. Are There Funding Sources Available for SEL Curriculum?
SEL programs can receive funding under the following programs:
- CRRSA (CARES Act 2) – With this funding source, schools can implement mental health and wellbeing support programs for students.
- Title IV Funding – Schools can develop and implement comprehensive programs that foster supportive, safe, and healthy environments that encourage student achievement using Title IV funding.
- Elementary and Secondary School Emergency Relief (ESSR) funds – Part of the Education Stabilization Fund in the CARES Act, schools can use the ESSR fund to allocate money to address students’ social, emotional, mental health, and academic needs as a result of the pandemic.
- Community Mental Health Services Block Grant – This grant provides funds to help communities develop comprehensive mental health services and to address needs in existing treatment services for individuals with severe mental health conditions.

Discover how Navigate360 SEL empowers educators, administrators, caregivers and students to take an active role in the social and emotional growth needed to turn students into happy, healthy and capable adults.
d. Common Challenges and Best Practices for Implementing SEL Curriculum
Common Challenges
There are many common challenges that districts and schools may come across in the process of developing SEL curricula, such as:
- An abundance of SEL frameworks from many different disciplines that complicates the process of choosing the right framework for your school
- Teachers who may not feel that they have the luxury of integrating social-emotional lesson plans in between teaching core academic curricula and getting students ready for standardized testing
- Inconsistent language between SEL frameworks that can make it difficult to understand what skills are being taught to students and how to measure success rates
- Lack of support for teachers and administrators who may need more guidance and mentorship during the early stages of SEL program implementation
Best Practices
Administrators and educators can work through these challenges by understanding the best practices of planning, developing and implementing an SEL program:
- Build the foundational elements – Create a committee that will develop the vision for your SEL program and collaboratively plan the implementation.
- Strengthen adult SEL – In schools where adult SEL is prioritized, the implementation of student-centric SEL is more effective. Schools should lead professional development courses for adult SEL. Additionally, educators should reflect on their own social-emotional competencies and put together strategies to model them in the classroom.
- Implement an SEL strategy for students – Put SEL into action. School curricula and programs should promote students’ social-emotional learning by fostering supportive learning environments, elevating student voices, and establishing equitable discipline policies. The SEL program should be delivered via technology, rather than using an analog, paper-and-pencil method, for greater and on-demand access
- Create ongoing SEL processes – The SEL program is a dynamic one that will need to be refined and evaluated regularly. Districts and schools should have a structured plan for collecting data, analyzing outcomes, and making adjustments.
- Create a shared SEL culture across stakeholders – Students, parents, caregivers, teachers, and other school staff should have a shared vocabulary and structure for talking about and reinforcing SEL skills.
e. What Is the Best Way to Deliver SEL Curriculum?
Students these days have always existed in a world filled with smartphones, boundless WiFi and social media. They are the first true digital natives. In fact, by age 12, nearly 70% of American students have a smartphone. That’s why an effective SEL program for Gen Z and Alpha students needs to meet the learning preferences and attention spans of these highly connected, digital-savvy generations.
Digital SEL platforms that create visually engaging, interactive lessons spanning videos, games, articles and other multimedia are exactly what today’s students are looking for. These programs deliver important lessons about character development, social-emotional learning, cyberbullying, mental health, college and career prep, and communication skills — and they do it in a digitally savvy way that keeps students engaged while teaching them crucial life skills. Additionally, with students able to access their lessons via a web-based platform or a mobile app, digital SEL programs are flexible to accommodate their busy, connected lifestyles.
Getting Started with SEL Curriculum
It’s clear that social-emotional learning positively impacts students’ futures academically, emotionally and socially. After all, if the goal of education is to help children become productive members of society, then ensuring they are well-rounded and emotionally intelligent is crucial.
Contact us today to learn more about Navigate360’s Social-Emotional Learning and Restorative Curriculum, the most effective way to engage students, staff and caregivers with the information they need to support a successful school career and future.

