Prepare Students for Success from the Start with SEL in Preschool
Preschool is often the beginning of formal education, setting children on a path to success. It is also the ideal time to begin incorporating social-emotional learning (SEL) that supports the development of the skills necessary to be not only good students, but also good citizens. SEL instruction is proven to help students navigate their emotions, form relationships and make responsible decisions. Implementing social-emotional learning for preschoolers will provide children the foundation they need to be successful socially, emotionally and academically.
As children grow and move through the various developmental stages of early childhood, they begin to develop social and emotional skills. It’s important to acknowledge that the pace of this progression will vary from child to child. However, this development can be encouraged through instruction that is designed specifically for preschool-aged children. It’s critical that preschool SEL curriculum be built on a research-based framework, such as CASEL.
CASEL Competencies
The Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning, known more broadly as CASEL, has established a framework of five core social and emotional competencies. These five competencies are the foundation for academic success, healthy relationships and mental health and wellness.
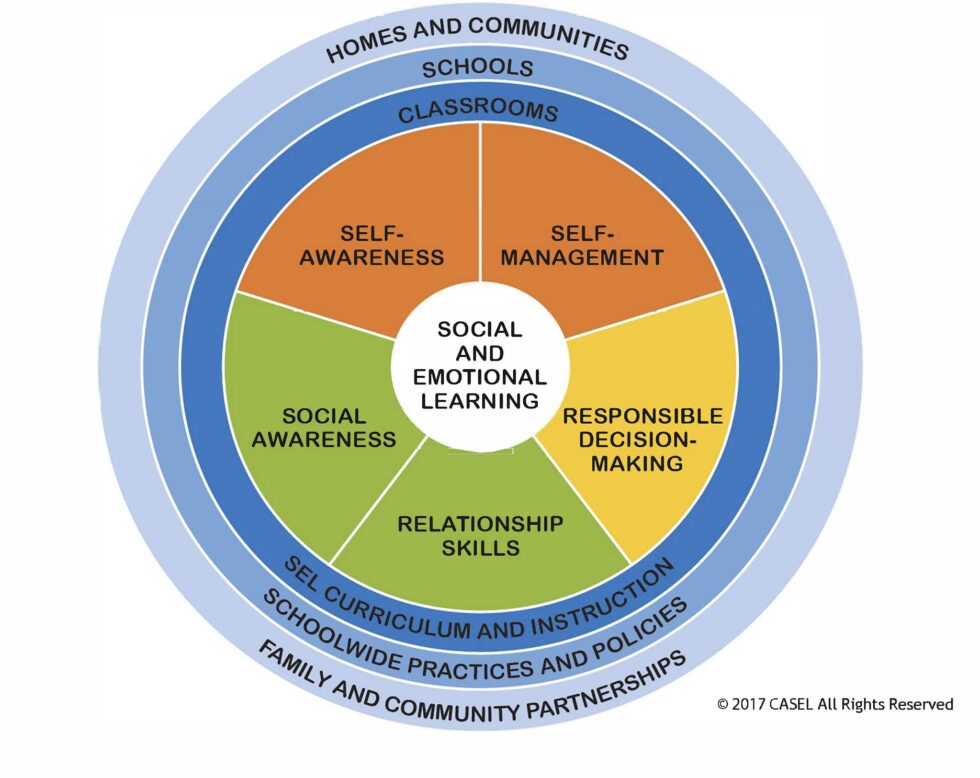
Children begin developing these skills in infancy, and in the preschool setting, they should be a central focus of learning. In order to engage children and communicate these foundational skills effectively, preschool SEL is often delivered through play rather than structured lessons.
SEL Milestones by Age
Age 3
- Beginning of self-regulation of emotions, such as calming down within a few minutes after a parent leaves
- Initiates play with other children
Age 4
- Imaginative/pretend play
- Seeks out other children for play
- Comforts others in distress
- Recognizes danger and avoids it, such as a hot stove or tall heights
- Willingly helps others/seeks out opportunities to be helpful
- Adapts behavior to environment, such as on a playground or in a library
Age 5
- Takes turns/follows rules in play
- Willingly sings, dances, or acts for others
- Demonstrates responsibility by participating in household/classroom chores, such as cleaning up
Source: https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/actearly/milestones/index.html
Using Play as Part of Preschool SEL
Preschool is where children begin to learn the processes and expectations necessary for their educational career. Responsibility, cooperation, empathy and more can all be taught in a fun way through routines, songs and games. Preschool-age children typically have a sense of curiosity about their environment, and SEL concepts can be included in most, if not all, activities in the classroom.
SEL in preschool through play can include:
- Identifying emotions in themselves, others and in pictures
- Cooperation with others, such as taking turns, following directions and asking for and giving help
- Developing vocabulary related to social situations, such as showing concern, expressing gratitude or being frustrated or angry
- Practicing word pairs such as near/far, same/different, can/cannot and so on
By making learning experiences fun and relevant, preschool teachers can help their young students develop and practice key social-emotional skills.
A Positive Climate Enhances Social-Emotional Learning for Preschoolers
In addition to teaching SEL through play, preschool teachers can create an environment in which SEL skills can grow and thrive. Routines are especially powerful for making a classroom feel comfortable and supportive. Children thrive with the predictability a routine provides, and routines for entering the classroom, circle time, snack time, cleaning up, recess and dismissal can provide that predictability every day.
Other ways to boost Preschool SEL skills:
- Posting your schoolwide and classroom behavior matrix outlining positive behavior expectations
- Involving all students in classroom routines
- Responding to negative behaviors with redirection
- Acknowledging positive behaviors as they happen
- Encouraging curiosity and wonder about the world around them
- Celebrating holidays and cultural traditions and learning about others
- Taking part in community events
- Using games, songs, and stories to reinforce SEL concepts
The structure of the preschool classroom enables very young students to actively learn basic SEL skills while engaging in play and participating in classroom routines.
PBIS and SEL in Preschool
For many schools, SEL can be an effective addition to a PBIS initiative. But can preschools use PBIS?
Absolutely! Preschoolers thrive on positive feedback, and a PBIS initiative makes it easy to recognize students for positive behavior. Creating a matrix of positive behavior expectations and what those behaviors look like in various situations can be incredibly impactful.
At the heart of a PBIS initiative is a token economy system. Recognition of positive behaviors, paired with tokens which can be exchanged for items or privileges, helps students to connect concepts with actions.
Recognizing positive student behavior at the moment it occurs is especially powerful for preschool-aged children. This positive recognition helps to build neural pathways that connect the reward centers of the brain with the action that triggered the recognition. Over time, positive recognition creates positive behaviors that are deeply ingrained.
Preschool SEL is an effective complement to a PBIS initiative. The core competencies of SEL can be mirrored in the expectations outlined in PBIS. For example, a common school value expressed in PBIS is “Be Respectful.” Respectfulness in the school environment can take various forms, such as “turning on your ears” when the teacher is speaking, throwing trash away and walking quietly in the hallway. These actions also help build SEL skills that correlate with competencies such as self-management, self-awareness and responsible decision-making.
Teaching Social-Emotional Learning in Preschool
Ultimately, preschool is a great place to begin deliberate instruction in SEL. It establishes a baseline for behavior and helps students to develop core interpersonal skills. It also enables students to build a foundation for positive mental health.
Social-emotional learning for preschools can have far-reaching effects over the course of a student’s educational career, including positively impacting academic performance, mental health and behavior for students at all ages. It also helps schools to establish equitable learning environments — every dollar invested in SEL produces an $11 return!
Navigate360, PBIS Rewards and SEL – A Powerful Synergy
Preschool social-emotional development can put students on a path towards a better educational experience. Including it as part of a PBIS initiative can boost its effectiveness. Together, preschool SEL and PBIS can create a learning environment that not only benefits students but also staff and families.
Navigate360 can help you set your littlest learners on a positive educational path with solutions that work holistically for safety, success and wellness. Our Suite360 curriculum includes relevant, age-appropriate and engaging lessons for students, support & professional development for staff and supportive and informational exercises for families. Our PBIS Rewards software suite enables schools to manage their PBIS initiative digitally and includes optional behavior intervention lessons that can be assigned during a referral.
Preschool SEL is just the beginning. Let Navigate360 help you create an educational environment in which every student can learn and grow – academically, socially and emotionally!