Set Students Up for Success
Provide essential support students need to navigate their stressors.
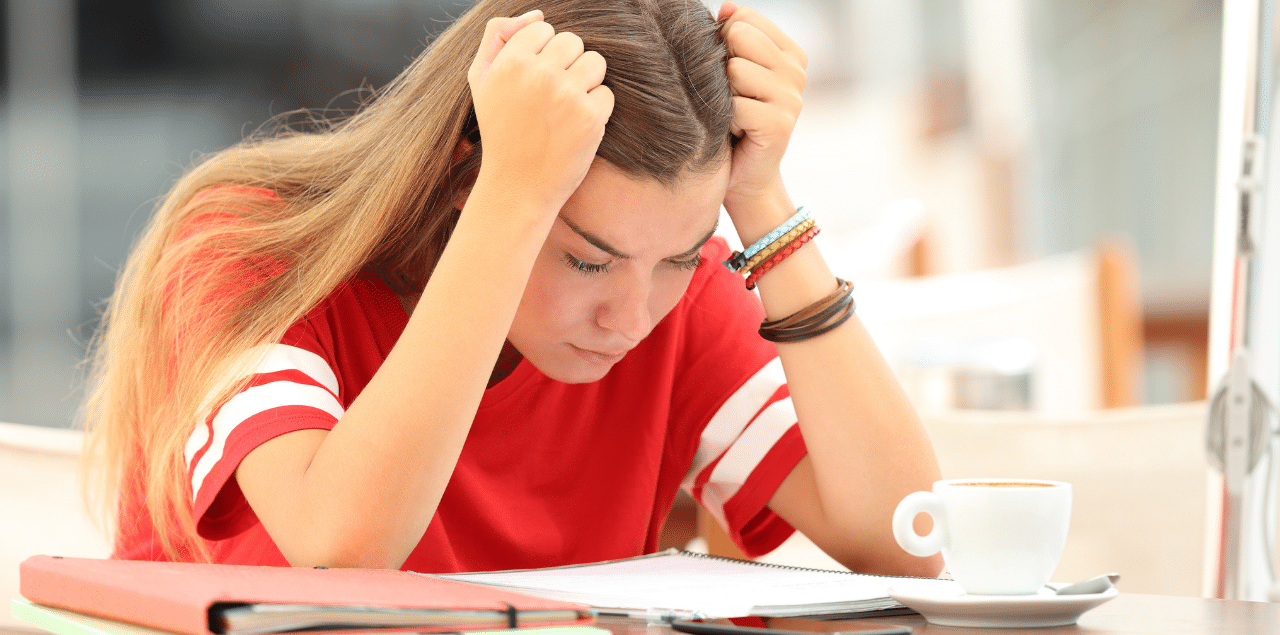
You’re likely already aware that students today are facing heightened mental health issues, including staggering rates of anxiety and depression. According to the CDC’s “Youth Risk Behavior Surveillance Data Summary and Trends Report: 2011-2021,” more than 4 in 10 (42%) students felt persistently sad and hopeless. Nearly one-third (29%) experienced poor mental health in 2021. Numerous factors contribute to adverse mental health for K-12 students, but perhaps one of the most prevalent is academic stress. Spanning all age groups and socioeconomic statuses, no student is immune to the pressure of academic performance. How does school affect mental health?
How Grades Affect Mental Health of Students of All Ages & Situations
Academic stress is often associated with high school students preparing for college, but younger students experience it as well. Students of all ages have to juggle the pressure to perform well academically with extracurriculars, homework, and standardized testing. And this is true for students in all socioeconomic situations, as well. In fact, a recent study found that students in affluent, high-achieving schools are equally at risk of developing behavioral and mental problems as students from disadvantaged backgrounds. This is essential knowledge for school psychologists, counselors, and administrators to provide proper mental health support for at-risk individuals.
Common Causes of School-Related Stress
Knowing the most common causes of school-related stress can help you provide distinct mental health support for students’ unique needs. K-12 students experience numerous factors that are barriers to mental wellness, including trauma, discrimination, poverty, and excessive pressure to excel.
Researchers have identified the following as the most common contributors to school-related stress:
- Demanding academic content and excessive homework
- High-stakes tests
- Pressure from parents to gain acceptance into prestigious universities
- Developmentally inappropriate classrooms
- Peer relationships
- Lack of preparation
- Academic kindergartens
- Overbooked schedules
- Pressure to maintain high grades and fear of failure
- Conflicts with teachers
- Transitioning to secondary school
- Poor diet and lack of sleep
While these are common causes of school-related stress, it’s important to note that every individual responds to stressors in different ways. The American Academy of Pediatrics cites development, experience, and a child’s individual temperament as factors that contribute to a child’s stress response. Age can play a role in stress response, as well; consider how something like a mid-year teacher change would be more stressful for a first-grader than a high school student. While there’s no such thing as a one-size-fits-all approach to mental health support for students, building skills like social-emotional learning (SEL) can help students of all ages and backgrounds handle stress better.
PBIS Rewards Joins Navigate360, Advancing Whole-Child Wellness & Safety!
Navigate360’s whole-child student safety and wellness suite offers the tools, expertise and confidence district leaders need to create safe, supportive school environments — and strengthen students’ academic performance. For the first time, educators can seamlessly connect students with situationally relevant resources that help them return to a pathway of wellness.
Learn MoreConsequences of Chronic Stress
Without the right mental health support in place, stress can become chronic, leading to a number of adverse outcomes for students such as:
- Physical illness
- Anxiety and depression
- Insufficient sleep
- Irritability or volatility
- Decrease in academic performance
- Social withdrawal
- Experimentation with drugs and alcohol
- Cheating
- Increased risk of self-harm
- greater risk of developing suicidal ideation
Often, these outcomes can create a vicious cycle for students who are already dealing with school-related stressors. For example, decreased academic performance as a result of school-related stress can worsen anxiety, leading to even worse academic outcomes. Insufficient sleep, anxiety, and irritability can also exacerbate the pressures of performing well on high-stakes tests and college interviews. And students often feel this pressure at home just as much as internally or in school. Consider the college admissions scandal termed Operation Varsity Blues, in which 33 parents paid more than $25 million in bribes to get their kids into top-tier universities—showing the extent of the lengths some parents will take to meet society’s high academic standards for kids.
The Fallout of COVID-19
Unfortunately, school-related stressors have only been worsened by the COVID-19 crisis. Educators across the globe are concerned about learning loss as a result of the pandemic, and rightly so. As students have returned to in-person learning, this learning loss has led to added pressure to “catch up” academically. Harvard and Stanford Universities’ collaborative research effort, the Education Recovery Scorecard, found that “the average U.S. public school student in grades 3-8 lost the equivalent of a half year of learning in math and a quarter of a year in reading” during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The COVID-19 crisis has also exacerbated many of the common causes of school-related stress noted above. For example, some educators assigned excessive homework during virtual learning to “make up” for time spent out of the classroom. They understandably struggled to teach virtual lessons effectively as they grappled with the pandemic themselves. Despite the realities of the pandemic, students were not exempt from the pressure to maintain high grades, even while dealing with things like limited access to digital devices and internet, sick family members, and poor diet without access to school meals.
How to Equip Students to Better Handle Stress
While schools can certainly take action to reduce causes of school-related stress at the source—revising testing and homework policies, shifting focus from grades to learning/understanding, and promoting physically healthy behaviors, for example—the reality is that school-related stressors can never be 100% eliminated. As such, every student needs to develop tools to help them navigate stress as well as other challenges. One effective way to make these tools available to students is through the intentional building of social-emotional learning (SEL) skills.
How Does SEL Help Relieve Academic Stress?
As a framework that helps students manage their emotions, improve their self-awareness, and develop positive self-identities, social-emotional learning is instrumental in reducing academic stress. SEL is a collection of skills that teach students how to navigate causes of school-related stress, like peer relationships, changes to environment, and pressure to perform. Fortunately, there are simple ways to implement social-emotional learning curriculum in schools.
In addition to school counselors, psychologists, and other school mental health professionals utilizing SEL strategies during counseling, SEL curriculum can also be implemented district-wide in classrooms and other group settings on school campuses. SEL curriculum provides tangible lessons with actionable tools and strategies, helping students become more comfortable with coping with academic stress. Lessons include topics such as creating goals, setting and enforcing boundaries, healthy strategies for dealing with stress, and effective communication tools. Through lessons around these topics and others like them, students develop their social-emotional learning skills, resulting in better academic, emotional, and social outcomes. And Navigate360’s research-backed, grade-specific SEL curriculum—Suite360—is delivered digitally, meeting students where they are for maximum learning and understanding. This gives districts and schools the flexibility of having these lessons completed asynchronously by students or led by school staff in a group or classroom setting.
Click here to learn more about our SEL curriculum, or schedule a consultation to have your questions answered and get the ball rolling on providing the essential social-emotional learning support students need to navigate their stressors—school-related and otherwise.