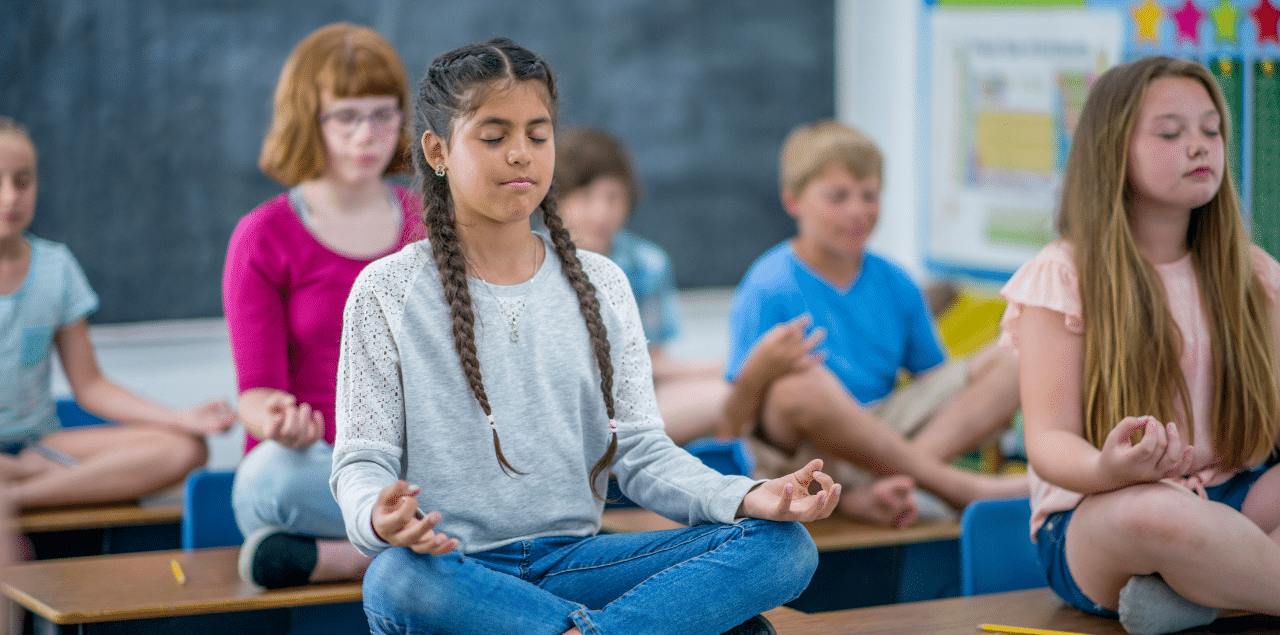
Mindfulness can serve as a key tool for students, teachers and administrators. However, it is important to note that there is no one-size-fits-all approach to incorporating mindfulness into education. There are various ways educators and school personnel can embed mindfulness practices into the classroom through social-emotional learning (SEL). This is partly because SEL curriculum addresses actionable skills, while mindfulness fosters the belief that each individual holds the innate ability to act on their SEL knowledge.
Additionally, students and educators may find that mindfulness can aid with character development and coping skills. Students may use mindfulness to calm their minds and bodies as they prepare for class or manage stressful situations. Teachers may use mindfulness practices to support their own mental health and avoid burnout. Administrators may also make use of these practices while managing stress and inspiring creativity. In order to achieve these things, mindfulness education is the first step.
Social-Emotional Learning & Mindfulness
Picture an instructor explaining the importance of “I” messages, encouraging students to practice this concept, and then moving on to another topic. The nature of SEL assumes that students are able to take these learned skills and apply them on their own.
As a tool of SEL, mindfulness assumes that each student has the natural ability to control their thoughts and actions and build relationships using innate qualities they possess, such as empathy and kindness. Mindfulness helps individuals calm their minds and bodies, making it easier to put SEL skills to use.
When weaving mindfulness practice into SEL, students may develop an awareness of and connection to their emotions and actions, resulting in better control over themselves and positive changes in their behavior, stress levels and relationships.
How to Practice Mindfulness in the Classroom
Common examples of practicing mindfulness in everyday life include yoga, Tai Chi, breathing exercises and meditation. But how can mindfulness be applied in a classroom setting? Educators can promote mindfulness in students by incorporating the following skills into their SEL curriculum:
- Begin class by having students reflect for one minute about gratitude or a good part of their day
- Listening with intention and understanding
- Showing interest in and making nonverbal connections with speakers
- Being cognizant of others’ emotions
- Allowing the speaker time to finish what he or she is saying
- Being aware of breathing while speaking
- Practicing belly breathing, breathing through the nose and using breathing to control emotions
- Ask students to visualize their breath as a color, noticing how it changes as they inhale and exhale
- Monitoring voice volume and intonation
- Watching gestures and body orientation
- Taking appropriate action when social violence presents itself
- End the class by asking students to reflect on something they learned that day, or something they thought went well
These actions have a psychological effect that can influence positive behavior change. When fostering mindfulness skills within SEL curriculum, students can have a more well-rounded understanding of how to handle conflict internally (by mindfully observing one’s own actions) and externally (by smartly navigating and processing their surroundings). Additionally, mindfulness can be a form of self-care, benefiting students proactively and regardless of conflict.
Addressing the Rise in Challenging Student Behaviors
In this webinar, Dr. Crystal Ladwig and Jeremy Tompkins from Escambia School District lead conversations that include mindfulness and how behavioral intervention and restorative practices can turn students’ challenging behavior into learning opportunities.
Proven Mindfulness Benefits for Students
The effects of mindfulness in K12 classrooms have been researched and have yielded positive results. Below are three studies that highlight how mindfulness can foster a positive school climate. These studies also explain how sample student populations participated in and benefited from mindfulness education.
Mindfulness Helps to Decrease Student Depression & Stress
In order to observe the benefits of teaching mindfulness in the classroom, 63 primary school children went through a five-week, school-based mindfulness program. Mindfulness practices in the study included belly breathing, breath awareness, and body scanning. Findings indicated that child-reported stress levels after the intervention were reduced. Overall, the study indicated that mindfulness in the classroom can help students deal with stress.1
Mindfulness Improves Teachers’ Perception of Student Behavior
Mindfulness education can greatly impact student behavior, as proven in a sample of 409 children from kindergarten through sixth grade at a Richmond, CA, public elementary school. The students participated in a five-week mindfulness-based curriculum that included learning mindfulness skills like careful listening to sounds in the classroom, whole body scan, “anchor words” to stay connected to breath, and discussion about thoughts and feelings, and results showed improvement in student behavior lasting up to seven weeks (reported by 17 teachers). This also shows that mindfulness in the classroom can help with teachers’ perceptions of student behaviors.2
Mindfulness Aids At-Risk Youth
An example of mindfulness helping to guide students to a safer life path can be seen when 27 at-risk young people participated in a weekly, 50-minute, semester-long ‘Learning to BREATHE’ program (an intervention program and substance abuse class). Mindfulness activities in this program include body scan, discussion on thoughts and feelings, and mindful breathing. Results concluded a decrease in depression and stress and an increase in the credibility of the program, in addition to a desire to continue the program.3
The Positive Effects of Mindfulness in the Classroom
According to Project AWARE Ohio from Miami University and Ohio Mental Health, “Mindfulness is only truly practiced when its three components — mindful awareness, mindful responsivity and mindful effort — are integrated and used together so that the full spectrum of positive effects can be experienced.” By practicing all these steps, students, teachers and administrators reduce stress and negative thoughts.
Benefits of mindful education and implementation may also include an increase in overall emotional health, self-compassion and a reduction in self-harm and stress. Mindfulness in the classroom has also proven to result in improved cognitive performance and engagement.
Mindful education proves to be a powerful way to help foster a positive and productive learning environment for teachers, administrators and students. Mindfulness in the classroom can also be incorporated into an SEL curriculum to help students successfully and safely navigate internal and external factors that impact their environment.
Integrating Mindfulness into SEL
Navigate360 SEL for Students is a dynamic program with a wide range of mindfulness topics integrated into its curriculum. Mindfulness lessons include Benefits of Practicing Mindfulness, Mindfulness and Meditation, Managing Anger Through Mindfulness, How to Unwind a Busy Mind, Mindfulness Test Preparation, and Using Mindfulness to Manage Stress. To learn more, contact us today.
1 Costello, E. & Lawler, M. (2014). An exploratory study of the effects of mindfulness on perceived levels of stress among school-aged children from lower socioeconomic backgrounds. Educational Disadvantage Centre, St. Patrick’s College, Dublin, Ireland.
2 Black, D.S. & Fernando, R. (2014). Mindfulness Training and Classroom Behavior Among Lower-Income and Ethnic Minority Elementary School Children. J Child Fam Stud.
3 Bluth, K., Roberson, P. N., & Gaylord, S. A. (2015). A Pilot Study of a Mindfulness Intervention for Adolescents and the Potential Role of Self-Compassion in Reducing Stress. Explore (New York, N.Y.), 11(4), 292–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.explore.2015.04.005